There’s a new hacking technique that focuses on Portuguese users. Abuse.ch shared on twitter the variant, Troystealer. “There seems to be a new stealer in town called #TroyStealer, targeting Portuguese internet users.”
There seems to be a new stealer in town called #TroyStealer, targeting Portuguese internet users ??
Exfil email address:
[email protected]Has anyone seen this threat before?
/cc @CNCSgovpt @sirpedrotavares pic.twitter.com/1bDK3BtYeE
— abuse.ch (@abuse_ch) June 12, 2020
As its name suggests, the information stealer is a Trojan specifically for collecting information from a system.
Troystealer utilizes various methods to achieve its goal. One way of acquiring confidential information involves the inputting of users’ keystroke. It could also access web-browsers and breaches login data like usernames and passwords, then sends it to another system by email.
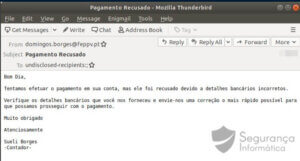
h/t: abuse.ch
Figure 1: Email template TroyStealer (in the Portuguese language).
Binary file
Threat name: TroyStealer.exe
MD5:DAB6194F16CEFDB400E3FB6C11A76861
SHA1:C76A9FB1A2AE927BF9C950338BE5B391FED29CD7
Imphash:F34D5F2D4577ED6D9CEEC516C1F5A744
Created: Thu Jun 11 19:53:24 2020
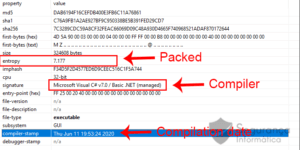
Figure 2: Compilation and packing details of TroyStealer malware.
The above shows the malware packed with (entropy 7.177) and created on the 11th of June via a .NET compiler.
Before executing the PE file, observing some details such as specific call references used to decrypt/unpacking the binary and execute another instance in memory via Process Injection technique.
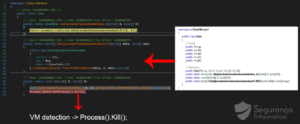
Figure 3: Process of unpacking the binary.
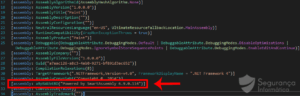
Figure 4: Smart Assembly 6.9.0.114 – used to obfuscate the binary.
“In detail, the malware detects if it is running inside a VM and stops the execution. In contrast, the malware is executed, and a new process created and executed using the process injection technique. After that, the harvesting process commences. Modules for collecting details from the browser as well as that to receive mail credentials from outlook begins operation.”
Filles accessed during the malware execution.
C:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\Mozilla\Firefox\profiles.iniC:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Login DataC:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\Mozilla\Firefox\profiles.iniC:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles\0i8ia8vs.default\logins.json
Deleted files during the malware execution
C:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles\0i8ia8vs.default\cookies.sqliteC:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles\0i8ia8vs.default\places.sqliteC:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\CookiesC:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Web DataC:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\History.
Getting security products, OS version, and Reg Keys
IWbemServices::ExecQuery – root\cimv2 : SELECT Caption FROM Win32_OperatingSystemIWbemServices::ExecQuery – root\SecurityCenter2 : SELECT * FROM AntivirusProductKey opened: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\PaltalkKey opened: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Windows Messaging Subsystem\Profiles\Outlook\9375CFF0413111d3B88A00104B2A6676.
The malware has to ascertain the presence of an internet connection before sending victim’s details via email. After which it establishes an SMTP communication with the authenticated email server.
The malware execution follows a series of steps to achieve its goal: getting the victim’s detail from browsers and email, getting HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Paltalk passwords; deleting browser-specific files, getting security products installed on your laptop; obtaining Operating system version, getting Keystrokes, and finally send the information via email to attacker.
Protective measures
Malware infiltrates every form of gathering and security available. It can be customized to resemble any government agency, streaming services, banks, etc. Some proactive measures you should take to avoid access to your system include: updating your software and removing all old, outdated softwares, thoroughly scan through emails before clicking on them; install an antivirus in your system, pay close attention to emails that might relate to your bank, Covid-19 or your workplace; access only secured sites, etc.
